An Introduction to Stamping Dies (Part One)
Stamping dies
A stamping die is special process equipment to manufacture parts by processing raw materials that are usually metal strips, which is also known as cold stamping die. The progressive die is composed of multiple steps; each step is completed in sequence, and a series of different steps are completed in one stroke of the punching machine. After a stroke is completed, the punch feeder moves the material forward according to a fixed pitch, so that multiple processes can be completed at the same time on one set of molds, generally including trimming, blanking, bending, expansion, shaping and adjustment. Stamping must have corresponding molds. Similar products can be realized by replacing parts in the same set of molds. The molds are precision-processed parts that are assembled. The manufacturing is single piece small batch production, which has features of great processing difficulty, high accuracy of mold parts (reaching 0.001 mm at this stage), high production technology requirements and high manufacturing costs (about 10% to 30% of product costs). Therefore, only when the stamping products are produced on a large scale, the advantages of stamping can be fully realized so as to obtain greater economic benefits. Stamping dies play a key role in the stamping and are very technology intensive products. The quality of stamping products, efficiency in the production process, and production costs are directly related to mold design and mold manufacturing. The technical level of design related to mold and manufacturing is one of the important standards to measure the level of a country's manufacturing industry, and determines quality of products, efficiency and development capabilities of new products to a large extent. There are various types of stamping dies, which can generally be classified according to the following main characteristics.
(1) Classifications according to the nature of the process
According to the nature of the process, cold stamping dies can be divided into punching dies, bending dies, drawing dies and forming dies. They are molds that separate the material strip and the waste material along the contour line of the waste material, such as blanking dies, punching dies, cutting dies, notching dies, trimming dies, cutting dies, etc.
The bending die is a die that causes the blank of the strip or the sheared material to be bent and deformed along a certain bending position to obtain a certain angle and shape of the part. Because the bending rebound is relatively great, it is generally designed to be over bent. Certain amount of great pressure will be applied at the bending position to compress the material belt.
The drawing die is a die that changes the height of the blank by pressure, or the thickness of the material is thinned and then stretched into an open hollow part, or the hollow part can be further changed into a part with a certain shape and size. Generally, the drawing part needs to be formed several times before it can meet the requirement. Drawing for once can have great deformation and the material is easy to crack. The forming mold is a mold that directly copies the raw material or semi-finished workpiece according to the shape and structure of the convex mold and concave mold, such as bulging molds, necking molds, flaring molds, undulating forming molds, flanging molds, shaping molds, etc., and the raw material only generates partial plastic deformation.
(2) Classifications according to the degree of the process combination
According to the degree of the process combination, stamping dies can be divided into process dies, compound dies, progressive dies and so on. Process dies refer to a stamping mold that completes only one process after opening and closing the mold once on the punching machine. Compound dies refer to the die with only one station. In one stroke of the punching machine, two or more processes are completed at the same station at one time, such as blanking bending dies and blanking drawing dies. The progressive die is the so-called continuous die. It has two or more stations in the feeding direction of the raw material. In one stroke of the punching machine, two or more processes are gradually completed in different stations. In the current production, this kind of mold is also used in large quantities.
Figure 1 is a typical structure of a blanking die, which is a single process die with guide posts and guide sleeves. It consists of two parts, an upper mold and a lower mold. The upper mold consists of 5 mold handles, 3 upper mold seats, 2 guide sleeves, 10 blanking punches, 8 backing plates, 7 fixing plates, 14 unloading plates, screws and pins. The lower mold is composed of 17 lower mold seats, 1 guide post, 11 cutting edges, 15 guide plates, 18 material receiving plates, screws, pins and other parts. The upper die is mounted on the press slider through the die handle 5, and reciprocates up and down with the slider, so it is called the movable part. The lower mold is fixed on the worktable of the press by locking the lower mold seat, so it is also called the fixed part.
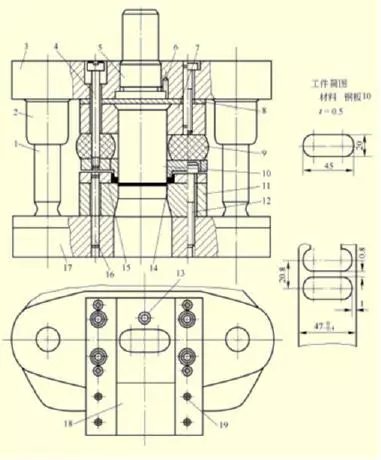
Figure 1 Typical single-process blanking die structure
Figures 2 and 3 are the progressive dies which are also called continuous dies. The standard die structure consists of 8 plates. Figure 2 is the mold's assembly, and Figure 3 is the mold's subassembly.

Figure 2 The assembly of progressive dies
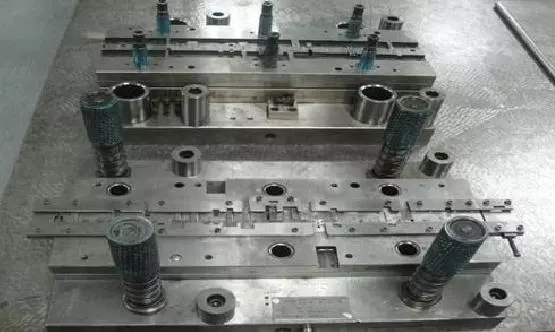
Figure 3 Separated parts of progressive dies
A stamping die is special process equipment to manufacture parts by processing raw materials that are usually metal strips, which is also known as cold stamping die. The progressive die is composed of multiple steps; each step is completed in sequence, and a series of different steps are completed in one stroke of the punching machine. After a stroke is completed, the punch feeder moves the material forward according to a fixed pitch, so that multiple processes can be completed at the same time on one set of molds, generally including trimming, blanking, bending, expansion, shaping and adjustment. Stamping must have corresponding molds. Similar products can be realized by replacing parts in the same set of molds. The molds are precision-processed parts that are assembled. The manufacturing is single piece small batch production, which has features of great processing difficulty, high accuracy of mold parts (reaching 0.001 mm at this stage), high production technology requirements and high manufacturing costs (about 10% to 30% of product costs). Therefore, only when the stamping products are produced on a large scale, the advantages of stamping can be fully realized so as to obtain greater economic benefits. Stamping dies play a key role in the stamping and are very technology intensive products. The quality of stamping products, efficiency in the production process, and production costs are directly related to mold design and mold manufacturing. The technical level of design related to mold and manufacturing is one of the important standards to measure the level of a country's manufacturing industry, and determines quality of products, efficiency and development capabilities of new products to a large extent. There are various types of stamping dies, which can generally be classified according to the following main characteristics.
(1) Classifications according to the nature of the process
According to the nature of the process, cold stamping dies can be divided into punching dies, bending dies, drawing dies and forming dies. They are molds that separate the material strip and the waste material along the contour line of the waste material, such as blanking dies, punching dies, cutting dies, notching dies, trimming dies, cutting dies, etc.
The bending die is a die that causes the blank of the strip or the sheared material to be bent and deformed along a certain bending position to obtain a certain angle and shape of the part. Because the bending rebound is relatively great, it is generally designed to be over bent. Certain amount of great pressure will be applied at the bending position to compress the material belt.
The drawing die is a die that changes the height of the blank by pressure, or the thickness of the material is thinned and then stretched into an open hollow part, or the hollow part can be further changed into a part with a certain shape and size. Generally, the drawing part needs to be formed several times before it can meet the requirement. Drawing for once can have great deformation and the material is easy to crack. The forming mold is a mold that directly copies the raw material or semi-finished workpiece according to the shape and structure of the convex mold and concave mold, such as bulging molds, necking molds, flaring molds, undulating forming molds, flanging molds, shaping molds, etc., and the raw material only generates partial plastic deformation.
(2) Classifications according to the degree of the process combination
According to the degree of the process combination, stamping dies can be divided into process dies, compound dies, progressive dies and so on. Process dies refer to a stamping mold that completes only one process after opening and closing the mold once on the punching machine. Compound dies refer to the die with only one station. In one stroke of the punching machine, two or more processes are completed at the same station at one time, such as blanking bending dies and blanking drawing dies. The progressive die is the so-called continuous die. It has two or more stations in the feeding direction of the raw material. In one stroke of the punching machine, two or more processes are gradually completed in different stations. In the current production, this kind of mold is also used in large quantities.
Figure 1 is a typical structure of a blanking die, which is a single process die with guide posts and guide sleeves. It consists of two parts, an upper mold and a lower mold. The upper mold consists of 5 mold handles, 3 upper mold seats, 2 guide sleeves, 10 blanking punches, 8 backing plates, 7 fixing plates, 14 unloading plates, screws and pins. The lower mold is composed of 17 lower mold seats, 1 guide post, 11 cutting edges, 15 guide plates, 18 material receiving plates, screws, pins and other parts. The upper die is mounted on the press slider through the die handle 5, and reciprocates up and down with the slider, so it is called the movable part. The lower mold is fixed on the worktable of the press by locking the lower mold seat, so it is also called the fixed part.

Figure 1 Typical single-process blanking die structure
Figures 2 and 3 are the progressive dies which are also called continuous dies. The standard die structure consists of 8 plates. Figure 2 is the mold's assembly, and Figure 3 is the mold's subassembly.

Figure 2 The assembly of progressive dies

Figure 3 Separated parts of progressive dies
Related News
- Design of Two-stage Overmolding for Automobile Headlight Cover
- Research on Stamping of Complex Aerospace Sheet Metal Components (Part Two)
- Research on Stamping of Complex Aerospace Sheet Metal Components (Part one)
- Design of the Upper Cover of a Household Air Conditioner Remote Control
- The Mold Cavity of Overmolding Handheld Forehead Thermometer Casing
- Overmolding Handheld Forehead Thermometer Shells
- Defects of Overmolded Lampshades
- An Introduction to Overmolding
- Overmolding Lampshades For Car Headlights
- Deformation of Plastic Components
News
Advantages
Low Cost
Topper leverages an offshore plastic mold making plant with a lower cost structure in order to offer lower pricing than Topper's competitors.
High Quality
Quick Turnaround
Topper leverages an offshore plastic mold making plant with a lower cost structure in order to offer lower pricing than Topper's competitors.
High Quality
Topper is ISO 9001:2008 certified, and Topper processing quality systems ensure that your parts are the highest quality possible for your applications.
Quick Turnaround
Topper offers three different shipping methods, including next day air, to accommodate your timing and budget requirements.
Online Quotes
Topper interactive online quotation system provides instant quotes for plastic mold making, injection molding, CNC machining and die casting.
Online Quotes
Topper interactive online quotation system provides instant quotes for plastic mold making, injection molding, CNC machining and die casting.

